PESTEL Analysis for Futuring: A Strategic Framework for Navigating Change
Part-11
By Rick Aman onColleges and organizations must continually assess and adapt to their external environment to envision and achieve their preferred future. This article series explores various strategic tools that aid in this vital process. In previous discussions, I examined Environmental Scanning to gather crucial insights about a region and explored how SWOT analysis can provide a snapshot of an organization’s current position. In this article, we will delve into another essential tool for futuring: PESTEL analysis.
PESTEL is a well-established and structured framework that allows organizations to systematically evaluate the external factors influencing their strategic decisions. By breaking down the complexities of the external environment into six key categories: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal. PESTEL provides a comprehensive lens through which organizations can anticipate changes and prepare for future challenges.
I will explore the definition of PESTEL, analyze its individual components, and discuss its application within futuring committees, particularly in conjunction with AI technologies. Additionally, I will compare PESTEL with environmental scanning to highlight its unique strengths and benefits. This exploration will demonstrate how PESTEL analysis not only enhances strategic foresight but also empowers organizations to navigate change with greater confidence and resilience. The most important factor to keep in mind while considering the value of PESTEL is its unique characteristic of highlighting potential trends permitting your organization to plan for the future. Trends will produce either headwinds or tailwinds for an organization. Recognizing the potential for headwinds or tailwinds can add valuable insights to a futuring process.
What is PESTEL Analysis?
PESTEL is an acronym representing six critical external factors of Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal that affect organizational planning. The framework is designed to help organizations understand trends in their environment and identify opportunities or risks. By organizing external influences into specific categories, PESTEL provides leaders with a clear picture of the factors they need to monitor and evaluate as they plan for the future.
The Six Elements of PESTEL Analysis
Political Factors Political factors involve government policies, regulations, trade agreements, and political stability. Changes in political leadership, tax policies, or regulatory frameworks can significantly impact industries. -- Example: New policies promoting renewable energy may alter the energy market, presenting both risks and opportunities for traditional energy companies.
Economic Factors Economic considerations include variables such as interest rates, inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. These elements determine consumer spending patterns, labor markets, and business growth potential. -- Example: An economic downturn could reduce employment yet increase the demand for colleges to provide skill and workforce training to update a workforce.
Social Factors Social factors encompass cultural trends, demographic changes, lifestyle shifts, and customer behaviors. Understanding these factors helps businesses align with evolving consumer expectations. -- Example: The aging population may increase demand for healthcare services, while younger generations might drive innovation in technology.
Technological Factors Technological considerations refer to the pace of technological advancements, digital innovation, and industry disruption. Organizations must monitor these developments to remain competitive. -- Example: Companies adopting artificial intelligence (AI) early gain a competitive edge by improving efficiency and customer experiences.
Environmental Factors Environmental factors include sustainability trends, resource availability, and ecological conservation efforts. Companies are increasingly expected to adopt sustainable practices to comply with regulations and align with public expectations. -- Example: Businesses that implement sustainable practices, such as reducing waste or conserving energy, are better positioned to meet evolving regulations and align with public expectations for environmental responsibility.
Legal Factors Legal may cover laws, regulations, intellectual property rights, and compliance requirements that impact operations. Adapting to new laws is essential for long-term stability. – Example: Changes to local building codes, such as stricter seismic standards in regions requiring contractors and developers to adjust designs and construction methods, impacting project budgets and timelines.
Characteristics of PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL analysis is a valuable tool for futuring because of several unique characteristics. It is comprehensive, covering six distinct areas to ensure that no external forces are overlooked. This thoroughness is complemented by a long-term focus, as PESTEL helps identify trends that may evolve over time, providing crucial insights for long-term planning. Additionally, the structured framework of PESTEL categorizes external factors, promoting systematic thinking and strategic alignment. This analysis tool also facilitates scenario development, allowing organizations to create multiple future scenarios that enhance their preparedness. Moreover, PESTEL is a dynamic tool that can be revisited regularly to capture new developments or changing trends. Together, these characteristics make PESTEL a powerful resource for strategic planning and futuring, enabling organizations to build resilience and agility in uncertain environments.
Using PESTEL in AI-Assisted Analysis and Futuring Committees
Artificial intelligence (AI) can significantly enhance PESTEL analysis by acting as an early brainstorming tool, allowing futuring committees to explore various scenarios more effectively. AI can analyze large datasets and identify hidden patterns in real time, providing insights that inform initial discussions. For instance, AI can process historical data to forecast future trends with greater accuracy, such as predicting shifts in consumer behavior. Additionally, AI tools can conduct sentiment analysis on public opinion related to political or social issues, offering valuable real-time insights. AI-powered models can run multiple simulations to explore different PESTEL-based scenarios, enabling committees to visualize potential outcomes. Furthermore, the automation of data collection from news sources, reports, and databases streamlines the process, saving valuable time for the futuring team. Overall, AI not only enhances the speed and accuracy of PESTEL analysis but also serves as a crucial resource for organizations focused on futuring.
In conjunction with AI, futuring committees typically are comprised of executive leadership, governing boards, subject-matter experts, and constituents with an interest in exploring future scenarios. Utilizing PESTEL analysis as a foundational tool guides their discussions. The process begins with data gathering, where the committee collects insights related to each PESTEL category, such as monitoring political developments, economic forecasts, and technological trends. By categorizing this information, the committee identifies significant trends in each area. They then build multiple future scenarios based on the insights from the PESTEL analysis, exploring various outcomes influenced by factors like economic growth. This structured approach ensures that the organization’s strategy is aligned with the most likely or preferred future scenarios identified through the analysis. Together, AI and PESTEL create a robust framework for strategic planning and foresight.
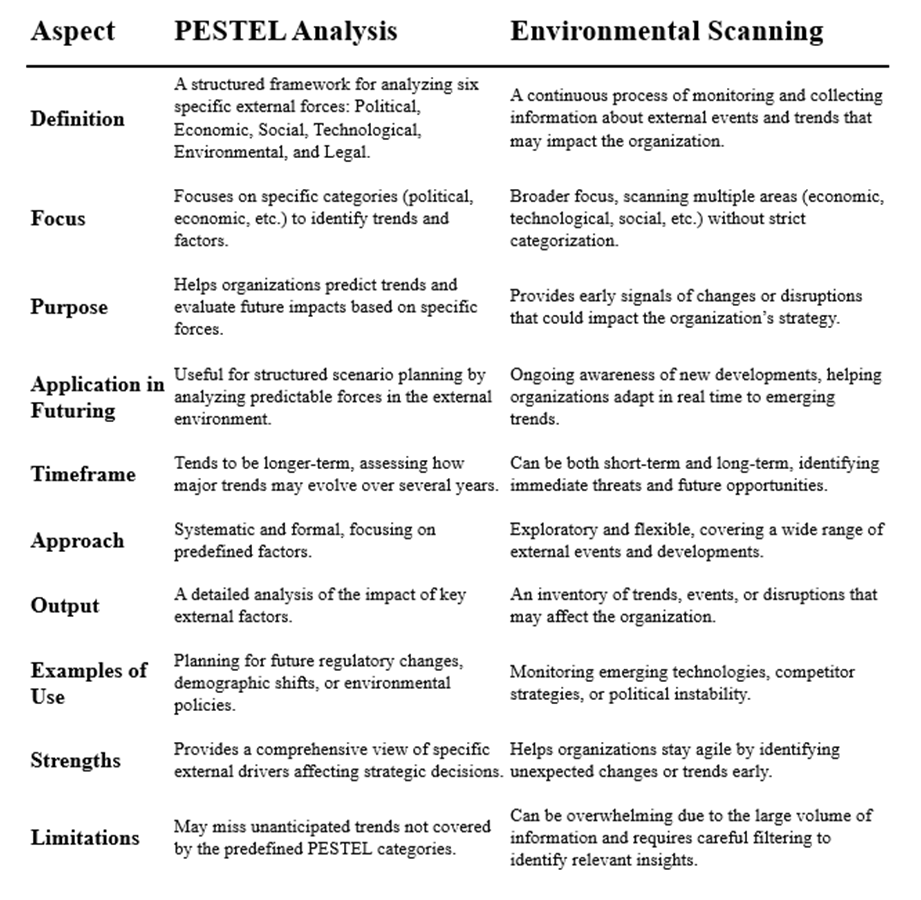
PESTEL analysis and Environmental Scanning are complementary tools used in strategic planning, but they differ in several ways. Below is a comparison:
Comparing PESTEL Analysis with Environmental Scanning
Compare and Contrast PESTEL with Environmental Scan
How PESTEL and Environmental Scanning Complement Each Other
Environmental scanning plays a crucial role in the strategic planning process by providing the raw data and insights that inform PESTEL analysis. This foundational step involves systematically gathering information about various external factors, which serves as the input for a comprehensive PESTEL evaluation.
PESTEL’s structured framework ensures that the insights derived from environmental scanning are not only organized but also actionable. By categorizing these insights into political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors, PESTEL helps organizations distill complex information into clear, strategic implications.
Together, environmental scanning and PESTEL create a dynamic and iterative planning process. Environmental scanning keeps organizations attuned to emerging trends and shifts in the external landscape, while PESTEL aligns these insights with long-term strategic objectives. This synergy enhances an organization’s ability to anticipate changes and adapt proactively, ultimately fostering resilience and informed decision-making in an ever-evolving environment.
Conclusion
PESTEL analysis is a powerful tool for futuring, enabling organizations to systematically evaluate external forces and develop future-ready strategies. Whether used by a futuring committee or enhanced with AI analysis, PESTEL helps identify trends, anticipate risks, and align strategies with future opportunities. While environmental scanning offers a broader, more exploratory approach, PESTEL’s structured framework ensures that critical factors are not overlooked.
By combining PESTEL with Environmental Scanning, organizations can stay agile, informed, and strategically aligned, ready to face the challenges and seize the opportunities of an uncertain future. Embracing futuring tools like PESTEL ensures that leaders are not just reactive but proactive, positioning their organizations for long-term success while creating a Strategic Visioning Document.
